Trending Topics:
- Blood Moon 2025
- Potoo Bird
- Cosmic Butterfly in Space
- Jupiter Juno
7 Mind-Blowing Facts Revealed by a 4,800-Year-Old Skeleton from Ancient Egypt
In a historic breakthrough, scientists have fully sequenced the DNA of a 4,800-year-old Egyptian man—unlocking powerful insights into ancient ancestry, migration, and daily life in early dynastic Egypt.
1/10

In a historic breakthrough, scientists have fully sequenced the DNA of a 4,800-year-old Egyptian man—unlocking powerful insights into ancient ancestry, migration, and daily life in early dynastic Egypt.
2/10

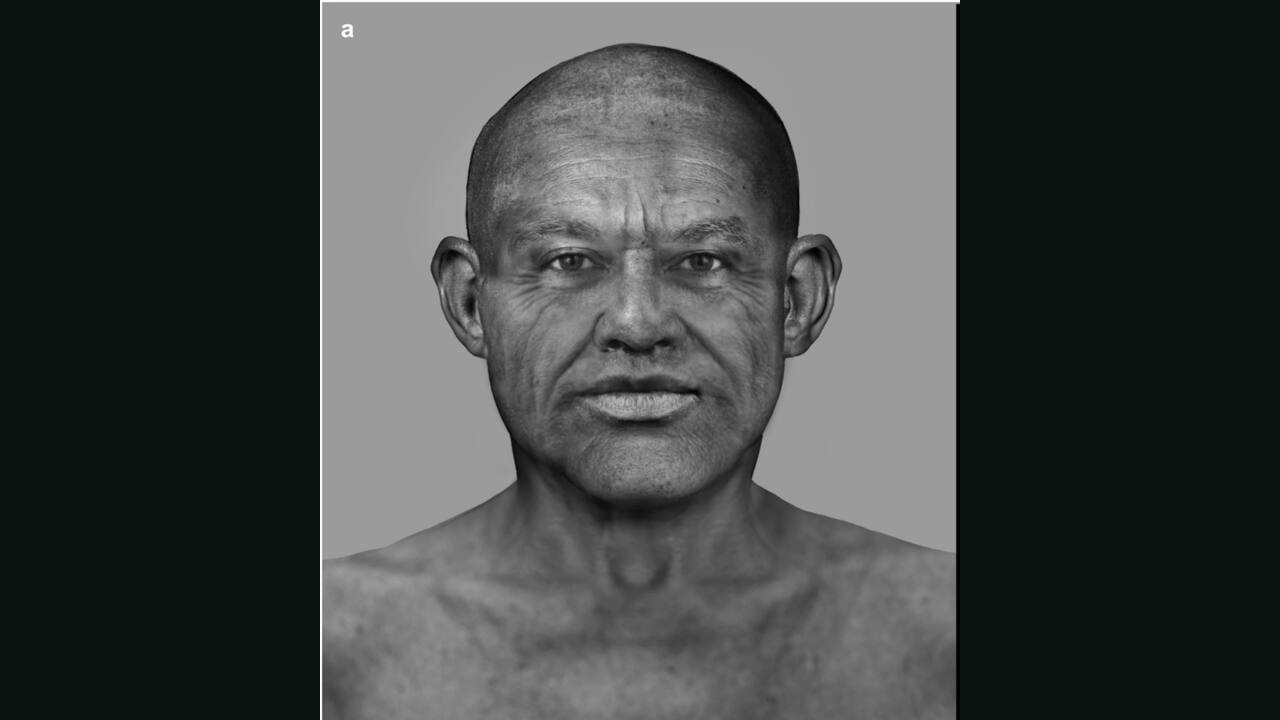
1. A COMPLETE ANCIENT EGYPTIAN GENOME: For the first time in history, researchers have successfully sequenced the entire genome of an ancient Egyptian individual. This milestone pushes beyond partial DNA analysis of mummies, offering a complete genetic map from a man who lived nearly five millennia ago.
3/10
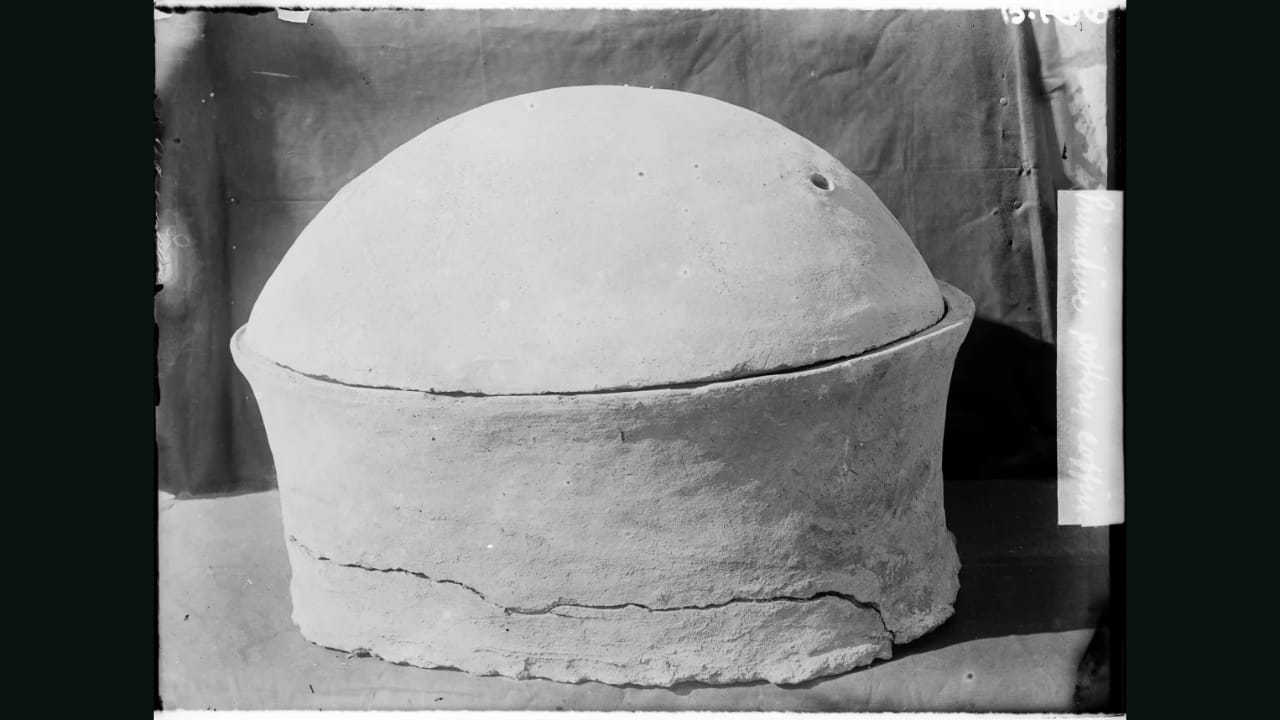
2. FOUND IN A CLAY POT: Unlike typical mummified remains, this man was buried in a sealed clay pot before embalming became the norm. The dry climate, consistent temperatures, and rock-cut tomb created a perfect environment for DNA preservation. Remarkably, it was the cementum layer of his tooth that held the most viable genetic material.
4/10

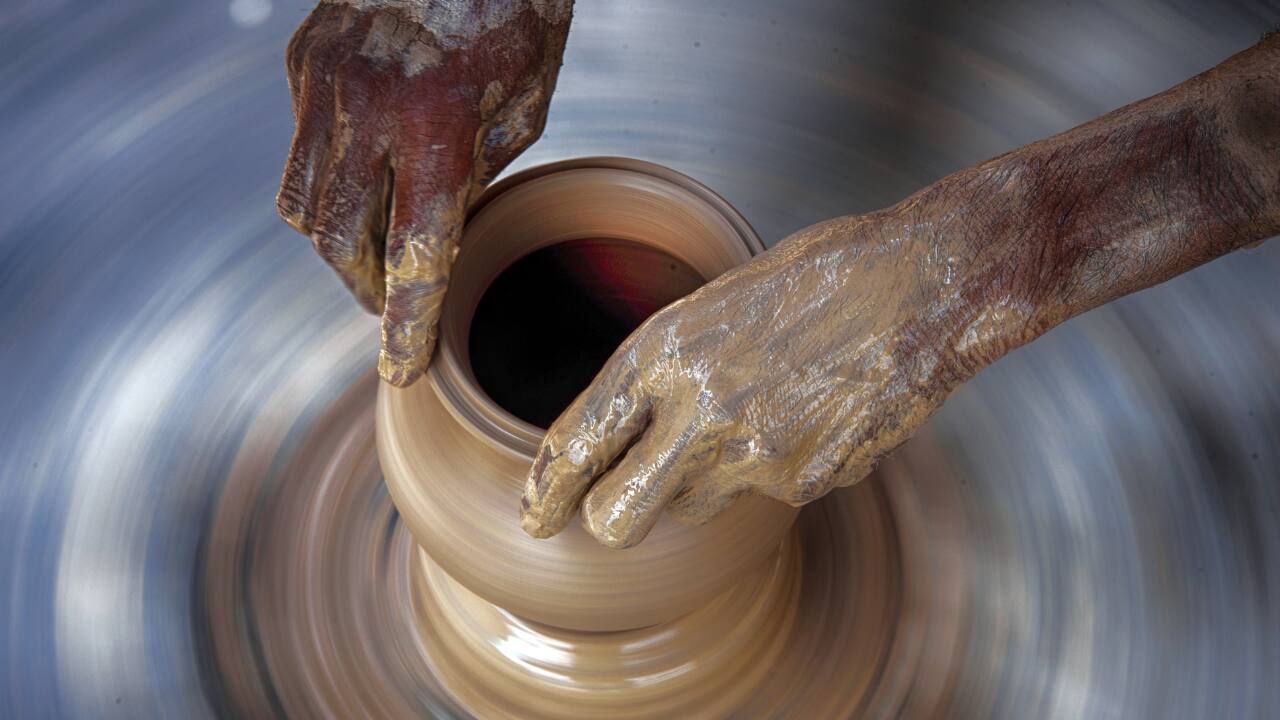
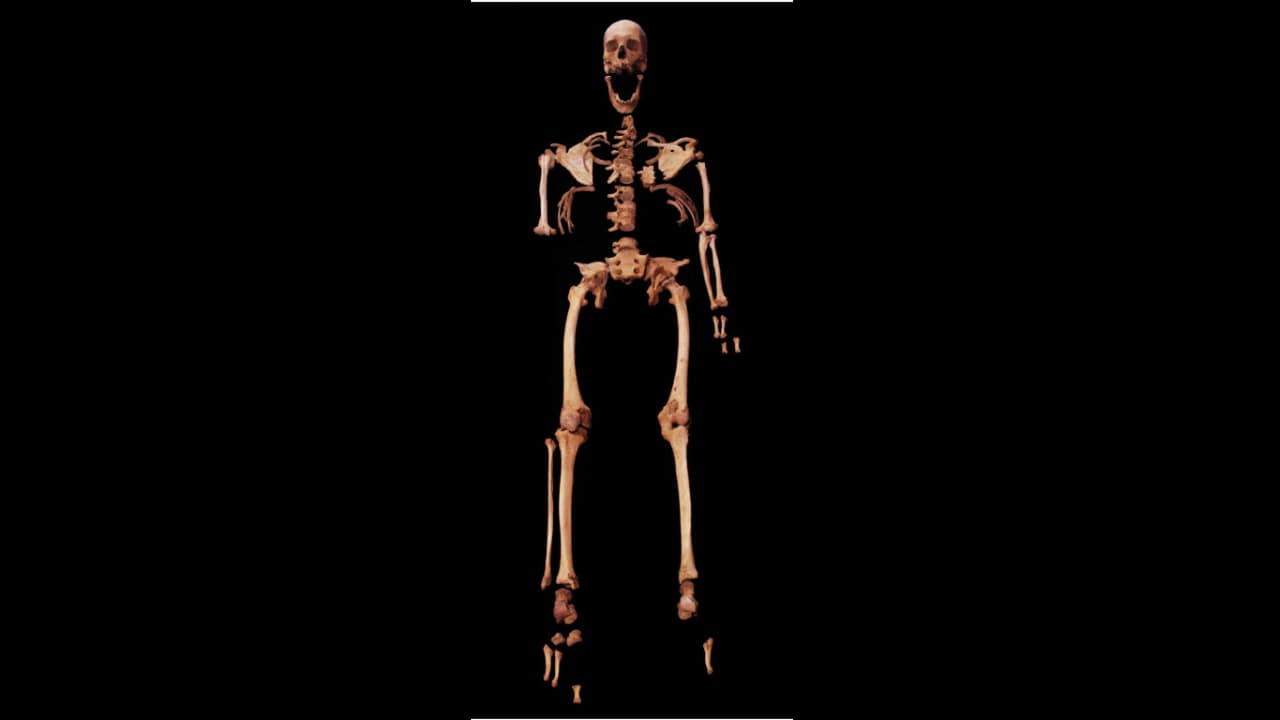
3. HE LIVED A HARDWORKING LIFE—POSSIBLY AS A POTTER: His skeleton tells the story of a physically demanding life. Signs of spinal compression, arthritis, and pelvic wear suggest long hours hunched over in a seated position—possibly crafting pottery with early wheels. These injuries reveal the toll of labor in ancient societies.
5/10

4. GENETICALLY NORTH AFRICAN—BUT WITH DEEP WEST ASIAN TIES: The genome reveals he was 80% North African, with the remaining 20% tracing back to West Asia and ancient Mesopotamia. This is direct evidence of early human migration and cultural exchange across the Fertile Crescent—something archaeologists have long theorized but never proved genetically.
6/10
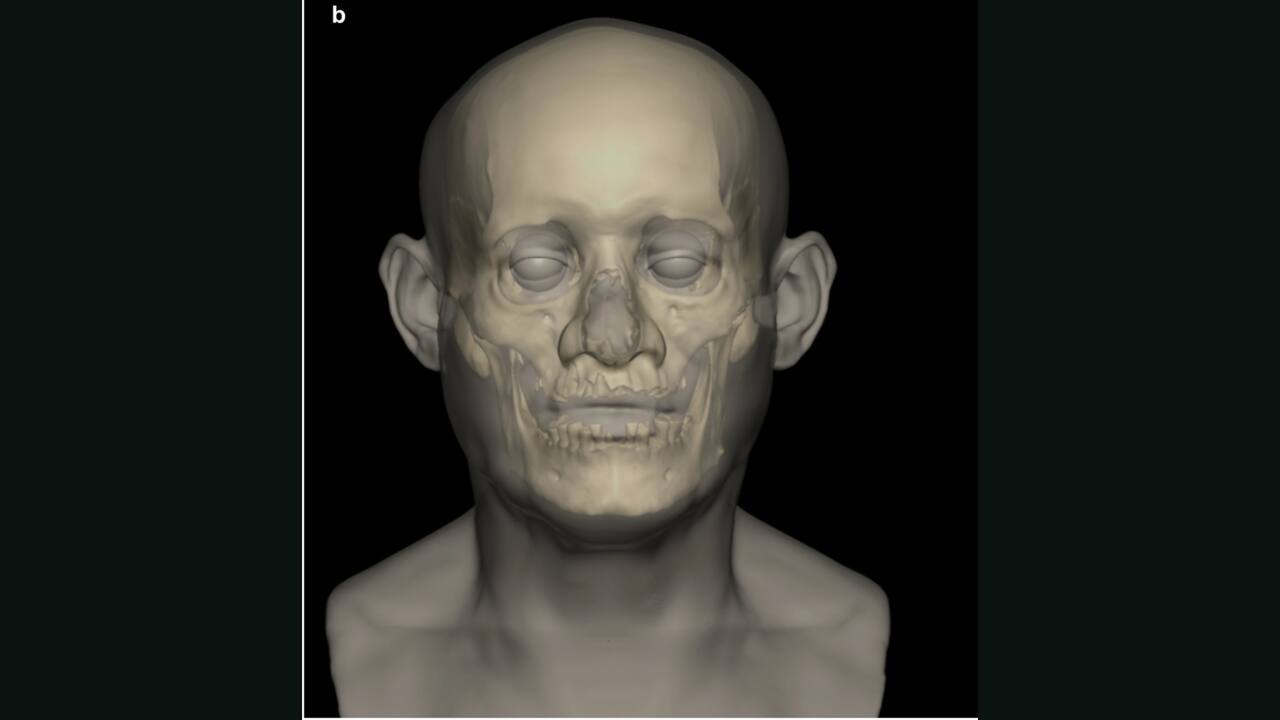
5. HE LIVED LONGER THAN MOST OF HIS TIME: Estimated to have died between the ages of 44 and 64, this man reached an impressive age for his era. His physical traits? Brown eyes, brown hair, and dark skin—features typical of North African populations at the time.
7/10
6. HE GREW UP BY THE NILE—AND ATE LIKE IT TOO: Isotope analysis of his teeth shows a diet of wheat, barley, native plants, animal proteins, and freshwater resources. His formative years were spent in the Nile Valley, reinforcing Egypt’s agricultural richness even in ancient times.
8/10

7. A NEW ERA IN ANCIENT DNA RESEARCH: Thanks to modern techniques like shotgun sequencing, scientists can now study full genomes rather than small DNA fragments. This discovery marks a turning point for Egyptology and ancient genetics, potentially rewriting our understanding of ancestry, trade, and migration during the earliest phases of Egyptian civilization.
9/10

Until now, ideas about ancient Egypt’s genetic links to neighboring regions were based on art, trade routes, and archaeological artefacts. This genome provides direct biological proof of cross-cultural connections that shaped one of the world’s greatest civilizations. As technology advances, we may soon uncover even more ancient Egyptian stories hidden deep in the bones of history.
10/10

Discover the latest Business News, Budget 2025 News, Sensex, and Nifty updates. Obtain Personal Finance insights, tax queries, and expert opinions on Moneycontrol or download the Moneycontrol App to stay updated!






