What is diabetic retinopathy: Symptoms, causes, and ways to prevent blindness
Diabetic retinopathy is a common diabetes-related eye complication caused by retinal changes. Risk factors include long diabetes duration, female gender, heredity, pregnancy, hypertension, smoking, obesity, and hyperlipidemia. Prevention involves strict blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol control, healthy lifestyle, medications, and regular ophthalmic screening to detect and manage early changes.
1/10

Layers of the eyeball
The eyeball is made up of three layers that cover it. The outermost is the fibrous layer that includes the sclera and the cornea, the middle is a vascular layer called urea, and the innermost layer is the neural part, known as the retina. The retina contains light-sensitive cells that are necessary for vision. (Image: Canva)
The eyeball is made up of three layers that cover it. The outermost is the fibrous layer that includes the sclera and the cornea, the middle is a vascular layer called urea, and the innermost layer is the neural part, known as the retina. The retina contains light-sensitive cells that are necessary for vision. (Image: Canva)
2/10

Diabetes and eye complications
Diabetes is a common condition seen in a number of adults, and it not only affects the blood sugar levels, but also causes various complications if not controlled timely. One such complication occurs in the eyes, and is known as diabetic retinopathy (DR).(Image: Canva)
Diabetes is a common condition seen in a number of adults, and it not only affects the blood sugar levels, but also causes various complications if not controlled timely. One such complication occurs in the eyes, and is known as diabetic retinopathy (DR).(Image: Canva)
3/10
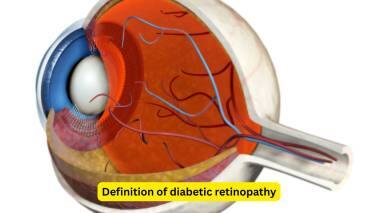
Definition of diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy refers to the retinal changes seen in people with diabetes mellitus, and is one of the common reasons, especially in Western countries, for blindness. The incidence of diabetic retinopathy is slowly on the rise, and appropriate attention is needed before complications occur.(Image: Canva)
Diabetic retinopathy refers to the retinal changes seen in people with diabetes mellitus, and is one of the common reasons, especially in Western countries, for blindness. The incidence of diabetic retinopathy is slowly on the rise, and appropriate attention is needed before complications occur.(Image: Canva)
4/10

Duration of diabetes as a factor
One of the most important determining factor for diabetic retinopathy is the duration of diabetes. Approximately fifty percent people who have diabetes mellitus develop this condition after ten years, and about ninety percent develop it after thirty years of its onset.(Image: Canva)
One of the most important determining factor for diabetic retinopathy is the duration of diabetes. Approximately fifty percent people who have diabetes mellitus develop this condition after ten years, and about ninety percent develop it after thirty years of its onset.(Image: Canva)
5/10

Gender and hereditary factors
The incidence of diabetic retinopathy is found to be more in females as compared to males, and there also exists a hereditary factor for this condition. It is transmitted through the parents as a recessive trait, and makes the person more susceptible to having retinopathy.(Image: Canva)
The incidence of diabetic retinopathy is found to be more in females as compared to males, and there also exists a hereditary factor for this condition. It is transmitted through the parents as a recessive trait, and makes the person more susceptible to having retinopathy.(Image: Canva)
6/10

Pregnancy and co-morbidities
It has also been found that pregnancy may accelerate the changes that are seen in diabetic retinopathy. Co-morbidities like raised blood pressure (hypertension) may increase the chances of this retinal disease. Poor metabolic control may also be a contributing factor.(Image: Canva)
It has also been found that pregnancy may accelerate the changes that are seen in diabetic retinopathy. Co-morbidities like raised blood pressure (hypertension) may increase the chances of this retinal disease. Poor metabolic control may also be a contributing factor.(Image: Canva)
7/10

Lifestyle influences
Certain other factors that can influence the changes of diabetic retinopathy include smoking and obesity. Hyperlipidemia, a condition in which high levels of fat particles (called lipids), like triglycerides and cholesterol, are present in the bloodstream, can also influence retinopathy changes.(Image: Canva)
Certain other factors that can influence the changes of diabetic retinopathy include smoking and obesity. Hyperlipidemia, a condition in which high levels of fat particles (called lipids), like triglycerides and cholesterol, are present in the bloodstream, can also influence retinopathy changes.(Image: Canva)
8/10

Blood sugar and metabolic control
Actively managing blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, and the blood pressure are necessary to prevent the changes of diabetic retinopathy. Consuming foods with a low-glycemic index, exercising regularly, and taking the medications as prescribed, can help in controlling diabetes.(Image: Canva)
Actively managing blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, and the blood pressure are necessary to prevent the changes of diabetic retinopathy. Consuming foods with a low-glycemic index, exercising regularly, and taking the medications as prescribed, can help in controlling diabetes.(Image: Canva)
9/10

Medications and supplements
Strict metabolic control of blood sugar and control of anemia (reduced haemoglobin) are necessary. Certain medications like protein kinase C inhibitors and ACE inhibitors may be prescribed by the healthcare provider. Antioxidants like vitamin E are also advised.(Image: Canva)
Strict metabolic control of blood sugar and control of anemia (reduced haemoglobin) are necessary. Certain medications like protein kinase C inhibitors and ACE inhibitors may be prescribed by the healthcare provider. Antioxidants like vitamin E are also advised.(Image: Canva)
10/10

Screening recommendations
Screening for diabetic retinopathy in people who have diabetes is important. It is recommended that people with diabetes, who have not had any changes of retinopathy, must follow up with the ophthalmologist once a year. For those with moderate type of non-proliferative DR, visit must be made every six months.(Image: Canva)
Disclaimer: This article, including health and fitness advice, only provides generic information. Don’t treat it as a substitute for qualified medical opinion. Always consult a specialist for specific health diagnosis
Screening for diabetic retinopathy in people who have diabetes is important. It is recommended that people with diabetes, who have not had any changes of retinopathy, must follow up with the ophthalmologist once a year. For those with moderate type of non-proliferative DR, visit must be made every six months.(Image: Canva)
Disclaimer: This article, including health and fitness advice, only provides generic information. Don’t treat it as a substitute for qualified medical opinion. Always consult a specialist for specific health diagnosis
Discover the latest Business News, Budget 2025 News, Sensex, and Nifty updates. Obtain Personal Finance insights, tax queries, and expert opinions on Moneycontrol or download the Moneycontrol App to stay updated!





