



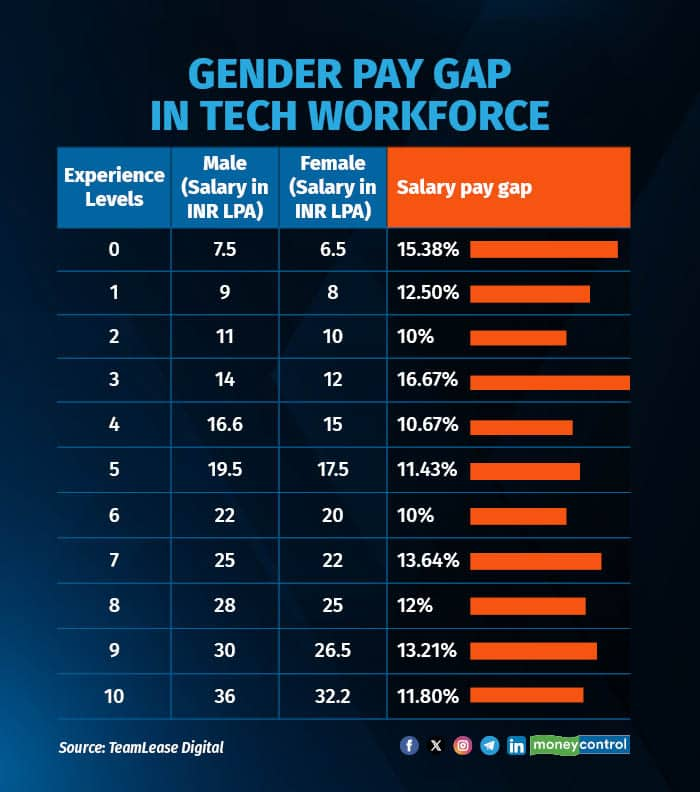
The gender gap in terms of pay has widened to an alarming level in the Indian tech space. The difference in salary between male and women employees in some job roles that see heavy demand has reached as high as 22-30 percent, shows a study by TeamLease Digital.
The difference is widest in roles like product manager, data scientist, fullstack engineer, data engineer and DevOps. Overall, the average pay gap across general tech roles is around 10-17 percent. Even at the fresher levels, women are earning nearly 15.38 percent less than their male colleagues.
According to the report, this is driven mainly by structural inequalities, disparity in role distribution, barriers in career advancement, and negotiation gaps. The pay gap varies across roles, with technical and leadership positions showing more significant disparities.
As women progress to higher positions, the gap only widens due to a lack of mentorship and fewer promotion opportunities, the report pointed out.
“Addressing the gender pay gap requires implementing transparent pay policies, establishing mentorship programmes, providing training on unconscious bias, and offering flexible working conditions to support work-life balance,” it said.
The IT sector has around 20.5 lakh women professionals. In Global Capability Centres (GCCs) of multinational companies, the percentage of women tech professionals is expected to increase from 25 percent to 35 percent by 2027, while women employees in GCCs count 4.82 lakh currently.

GCCs paying more
The TeamLease report mainly highlighted that the rapid expansion of GCCs in the country has led to engineers earning at least 12-20 percent higher salaries as compared to tech roles in IT products and services companies.
To give a comparison for software developer roles, GCCs are paying Rs 9.7 LPA (lakhs per annum) which can go up to Rs 43 LPA at a senior level with over eight years of experience. IT products and services sector salaries for the same role at an entry level pays about Rs 5.7 LPA and goes up to Rs 17.9 LPA with more than eight years of experience.
The report highlighted that the 1,600 GCCs in India have employed over 1.66 million professionals, with 800 more GCCs set to come up in the next five-six years, increasing India’s prominence as a global tech hub. Many of these GCCs will be set up in tier-II cities like Kolkata, Ahmedabad, and Vadodara, driving geographical diversification and employment in these locations.
Discover the latest Business News, Sensex, and Nifty updates. Obtain Personal Finance insights, tax queries, and expert opinions on Moneycontrol or download the Moneycontrol App to stay updated!
Find the best of Al News in one place, specially curated for you every weekend.
Stay on top of the latest tech trends and biggest startup news.