Understanding palatine tonsils and tonsillitis: Structure, function, symptoms, and treatment
Palatine tonsils protect against infections by detecting and destroying pathogens. Most active in children, tonsils can become inflamed, causing tonsillitis—acute or chronic—due to viruses or bacteria. Symptoms include sore throat, fever, and swelling. Treatment involves rest, fluids, and antibiotics if bacterial infection is suspected.
1/10

Palatine Tonsils Overview
Palatine tonsils are ordinarily ovoid shaped masses of lymphoid tissue that are present in the middle part of your throat, behind the oral cavity. They are supplied by five arteries and they function as the sentinels, providing protection against viruses, bacteria and other antigens that may enter the cavity.(Image: Canva)
Palatine tonsils are ordinarily ovoid shaped masses of lymphoid tissue that are present in the middle part of your throat, behind the oral cavity. They are supplied by five arteries and they function as the sentinels, providing protection against viruses, bacteria and other antigens that may enter the cavity.(Image: Canva)
2/10
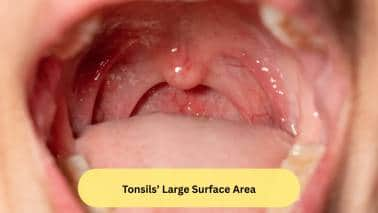
Tonsils’ Large Surface Area
Tonsils have a large surface area because of the presence of crypts. When any foreign pathogen enters the oral cavity, it comes in contact with the tonsils. On stimulation, certain cells known as the B-cells get activated, turn into plasma cells, and through various processes destroy the bacteria and viruses.(Image: Canva)
Tonsils have a large surface area because of the presence of crypts. When any foreign pathogen enters the oral cavity, it comes in contact with the tonsils. On stimulation, certain cells known as the B-cells get activated, turn into plasma cells, and through various processes destroy the bacteria and viruses.(Image: Canva)
3/10

Immune Surveillance Role
The tonsils also serve a surveillance function. They identify any intrusive antigens and begin alerting the body, so as to cause a widespread response with the help of antibodies. The tonsils have been known to be the most active from four to ten years of age, and start to involute after puberty.(Image: Canva)
The tonsils also serve a surveillance function. They identify any intrusive antigens and begin alerting the body, so as to cause a widespread response with the help of antibodies. The tonsils have been known to be the most active from four to ten years of age, and start to involute after puberty.(Image: Canva)
4/10

Types of Tonsillitis
The inflammation of tonsils is known as tonsillitis, and it may be acute or chronic in nature. Acute can be of various types like superficial, follicular, parenchymatous or membranous tonsillitis. It often affects children in the school-going age group, but it can affect adults as well.(Image: Canva)
The inflammation of tonsils is known as tonsillitis, and it may be acute or chronic in nature. Acute can be of various types like superficial, follicular, parenchymatous or membranous tonsillitis. It often affects children in the school-going age group, but it can affect adults as well.(Image: Canva)
5/10

Common Bacterial Causes
One of the most common bacteria responsible for acute tonsillitis is Haemolytic streptococcus. Others include staphylococci and pneumococci, or even H. influenzae. These bacteria may either affect the tonsils primarily or cause infection following a viral attack.(Image: Canva)
One of the most common bacteria responsible for acute tonsillitis is Haemolytic streptococcus. Others include staphylococci and pneumococci, or even H. influenzae. These bacteria may either affect the tonsils primarily or cause infection following a viral attack.(Image: Canva)
6/10

Typical Symptoms
The affected individual may present with a sore throat and difficulty in swallowing. In case of children, they may refuse to eat meals due to pain in the throat. Fever is common, and can vary from 38 to 40 degrees centigrade. Chills and rigors may also be seen.(Image: Canva)
The affected individual may present with a sore throat and difficulty in swallowing. In case of children, they may refuse to eat meals due to pain in the throat. Fever is common, and can vary from 38 to 40 degrees centigrade. Chills and rigors may also be seen.(Image: Canva)
7/10

Ear Pain and Complications
Pain in the ear can be due to tonsillitis, however, it may also be seen because of middle ear infection, which is a complication of acute tonsillitis. Other symptoms like headache, general body ache, malaise and constipation may also be observed in such cases.(Image: Canva)
Pain in the ear can be due to tonsillitis, however, it may also be seen because of middle ear infection, which is a complication of acute tonsillitis. Other symptoms like headache, general body ache, malaise and constipation may also be observed in such cases.(Image: Canva)
8/10

Physical Examination Signs
On examination, a foul smell may be noticed from a person who has tonsillitis. The tongue may be white or discoloured, due to bacterial buildup. The tonsils may become red and swollen, and yellowish spots can be seen which contain pus. A whitish membrane can also be seen over the tonsils in some cases.(Image: Canva)
On examination, a foul smell may be noticed from a person who has tonsillitis. The tongue may be white or discoloured, due to bacterial buildup. The tonsils may become red and swollen, and yellowish spots can be seen which contain pus. A whitish membrane can also be seen over the tonsils in some cases.(Image: Canva)
9/10

Treatment Recommendations
The affected person is asked to rest, and drink plenty of fluids, especially water. The doctor may prescribe some analgesics like aspirin or paracetamol, according to the age of the person to relieve the pain and reduce fever. Antibiotics may also be given if bacterial infection is suspected.(Image: Canva)
The affected person is asked to rest, and drink plenty of fluids, especially water. The doctor may prescribe some analgesics like aspirin or paracetamol, according to the age of the person to relieve the pain and reduce fever. Antibiotics may also be given if bacterial infection is suspected.(Image: Canva)
10/10

Consider Home Remedies
Warm liquids like herbal teas and broths can help soothe the throat when one has tonsillitis. Saltwater gargles are often recommended at least twice or thrice a day. Honey can help in soothing the irritation in the throat, and steam inhalation can also help in relieving the symptoms of acute tonsillitis.(Image: Canva)
Warm liquids like herbal teas and broths can help soothe the throat when one has tonsillitis. Saltwater gargles are often recommended at least twice or thrice a day. Honey can help in soothing the irritation in the throat, and steam inhalation can also help in relieving the symptoms of acute tonsillitis.(Image: Canva)
Discover the latest Business News, Budget 2025 News, Sensex, and Nifty updates. Obtain Personal Finance insights, tax queries, and expert opinions on Moneycontrol or download the Moneycontrol App to stay updated!






