



Google on December 9 unveiled the Willow, its latest quantum chip, marking a milestone in the development of quantum computing.
The tech giant claims that the chip is capable of solving a problem in just five minutes that would take the world's fastest supercomputers 10 septillion years (that’s 10,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 years).
Here's look into what Willow is, how it works, and why it could shape the future of technology.
What is quantum computing?
Quantum computing uses the principles of quantum mechanics to solve problems that are beyond the capabilities of traditional computers. While traditional computers use bits to process information as either 0s or 1s, quantum computers use qubits, which can represent both 0 and 1 simultaneously, thanks to a phenomenon called superposition.
This allows quantum computers to perform many calculations at once, allowing them to solve complex problems much more efficiently.
Five minutes vs 10 septillion years
One of the most impressive achievements of the Willow is its ability to perform a random circuit sampling (RCS) benchmark in less than five minutes. The company claims that this same computation would take the world’s fastest supercomputer, Frontier, around 10 septillion years.
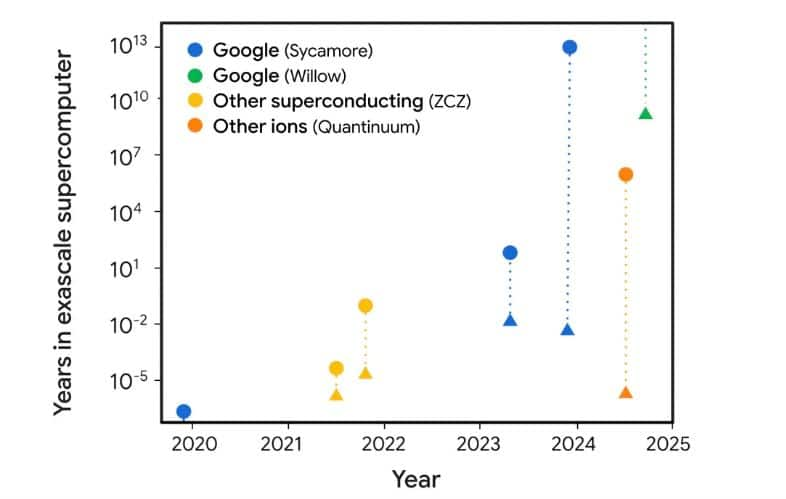
To put that in perspective, 10 septillion years is longer than the age of the universe itself.
Quantum error correction
One of the biggest challenges in quantum computing has been quantum error correction. Qubits, the fundamental units of quantum computers, are prone to errors as they tend to interact with their environment. The more qubits are used, the higher the chances of errors.
With Willow, Google claims to have made a breakthrough in error correction by demonstrating a reduction in errors exponentially as more qubits are added. Testing arrays of physical qubits, Willow showed that it could reduce error rates by half each time, reaching a historic achievement of being "below threshold".
"We tested ever-larger arrays of physical qubits, scaling up from a grid of 3x3 encoded qubits, to a grid of 5x5, to a grid of 7x7 and each time, using our latest advances in quantum error correction, we were able to cut the error rate in half," Hartmut Neven, founder, Google Quantum AI, said.
This means Willow is capable of scaling up while maintaining error-free computations, a step towards building scalable quantum computers.
Design and engineering
The Willow chip was made at Google's Santa Barbara facility, designed for quantum chips.
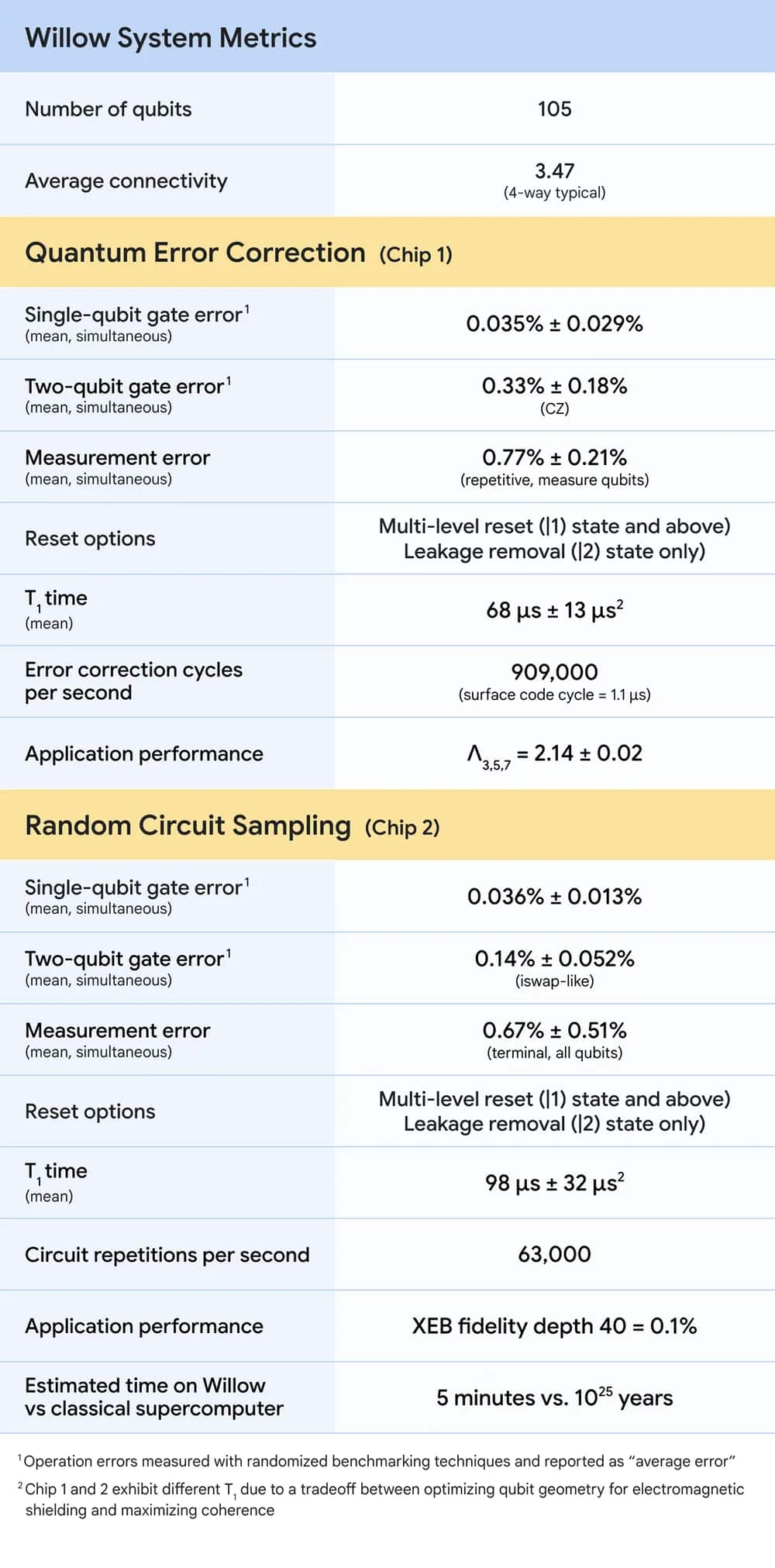
The chip contains 105 qubits, with key performance metrics such as T1 times (which measure how long qubits retain their state) improving by about five times over previous generations.
"We’re focusing on quality, not just quantity, because just producing larger numbers of qubits doesn’t help if they’re not high enough quality," Neven said.
What does Willow mean for the future?
While Willow’s achievements are significant, the next challenge for quantum computing is to demonstrate useful, beyond-classical computations, real-world problems that quantum computers can solve.
Google believes that Willow will help achieve this goal, particularly in fields like AI, medicine, energy systems and fusion energy research.
Also read | AI hits a speed bump: Why the next big thing isn't coming so fast
"My colleagues sometimes ask me why I left the burgeoning field of AI to focus on quantum computing. My answer is that both will prove to be the most transformational technologies of our time, but advanced AI will significantly benefit from access to quantum computing," Neven added.
Crypto killer?
While quantum computing holds immense potential for revolutionising fields like AI and medicine, it also poses a significant threat to the cryptocurrency industry.
The fear lies in the possibility of quantum computers breaking the encryption that secures digital assets.
A former senior product manager at Google, Kevin Rose, said on the X platform, formerly Twitter, that Google's Willow, is still far from posing a direct threat to cryptocurrencies.
He said breaking bitcoin's encryption would require a quantum computer with an estimated 13 million qubits to achieve decryption within a 24-hour timeframe. "In contrast, Google's Willow chip, while a significant advancement, comprises 105 qubits. We have a ways to go... Nonetheless, this is a remarkable leap forward in quantum computing," Rose said.
Discover the latest Business News, Sensex, and Nifty updates. Obtain Personal Finance insights, tax queries, and expert opinions on Moneycontrol or download the Moneycontrol App to stay updated!
Find the best of Al News in one place, specially curated for you every weekend.
Stay on top of the latest tech trends and biggest startup news.