



By Vaibhav Chowdhary and Vivek Jha
India heavily relies on fossil fuels, with coal accounting for 45 percent of its primary energy demand, followed by petroleum (25 percent) and biomass (20 percent) (IEA 2023). This dependence leads to high import rates for crude oil, coal, and natural gas, contributing to geopolitical risks and a significant fiscal deficit. Fossil fuels also contribute to 75 percent of India’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (Mukherjee & Chatterjee, 2022). While renewable energy is expanding, hard-to-abate sectors like steelmaking and oil refining remain challenging to decarbonize.
Hydrogen- A clean Molecule
To address growing emissions and enhance energy security, India requires a domestically produced, low-carbon fuel that can reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels. Hydrogen presents a promising solution due to its versatility, as it can be used both as a fuel and an industrial feedstock. Its clean-burning properties, meaning it produces only water vapor when combusted, make it an ideal candidate for decarbonizing various sectors. In 2021, India produced around 6 million tonnes of hydrogen (IEA, 2022), primarily using emissions-intensive methods such as steam methane reforming (SMR) and coal gasification. These processes, though widely used, release significant amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, counteracting the environmental benefits of hydrogen.
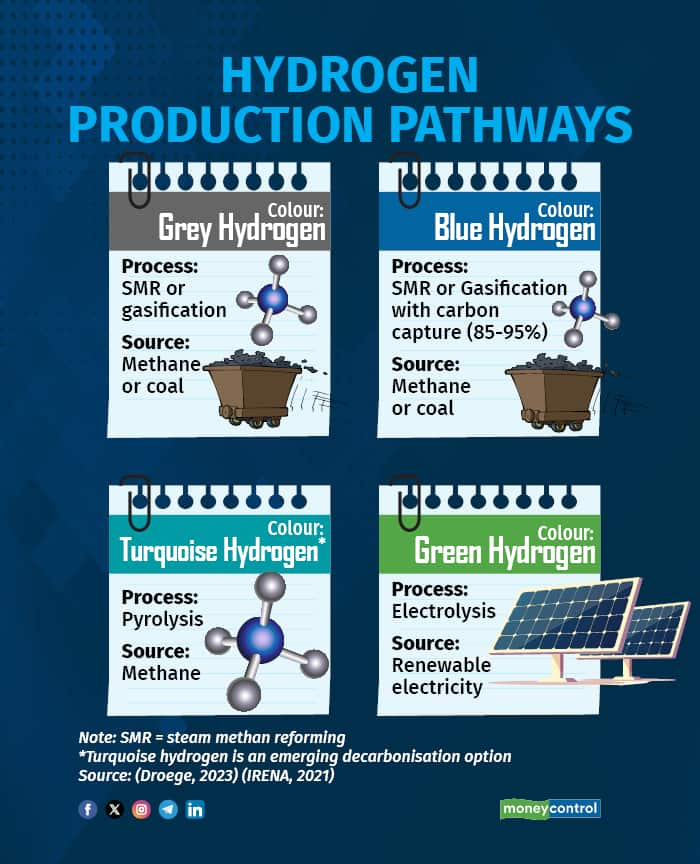
However, cleaner alternatives for hydrogen production exist. Green hydrogen is produced through water electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind, or nuclear power. This method does not emit carbon dioxide, making it a vital tool for achieving net-zero goals. Another low-carbon option is blue hydrogen, which is produced through SMR or coal gasification, but with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies that trap and store the emitted CO2. While blue hydrogen reduces emissions compared to traditional methods, it still depends on fossil fuels. Therefore, the long-term focus is on scaling up green hydrogen production, which aligns with India's renewable energy ambitions and offers a more sustainable solution for decarbonizing industries such as steelmaking, oil refining, and heavy transport.
In January 2023, India launched the NGHM with a $2.4 billion budget to develop green hydrogen and bridge the gap between green and grey hydrogen. By 2030, it aims to produce 5 million tonnes of green hydrogen annually, create 600,000 jobs, attract $100 billion in investments, and reduce fossil fuel imports by $12.5 billion. The focus is on sectors like oil refining, fertilizers, steelmaking, and heavy transport.
Policy Recommendations
The Government of India (GoI) has set a clear ambition to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070, with a focus on decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors. However, developing a green hydrogen ecosystem faces challenges. To overcome these, several actions are necessary. First, the GoI must harmonize standards and remove regulatory barriers to facilitate future hydrogen projects. This would create a favourable environment for investment. Additionally, stringent sectoral emission norms with incentives for both producers and consumers can drive progress, alongside a domestic marketplace for hydrogen-ready equipment across the value chain.
On the supply side, scaling green hydrogen production will require increasing full load hours (FLH) for electrolysers by enhancing renewable energy (RE) availability. Combining solar, wind, energy storage, and Round-The-Clock (RTC) power can significantly improve FLH, lowering the cost of green hydrogen. Studies show that a mix of onshore wind and solar power, even without storage, can provide high-capacity utilization at low costs in India (Tongia, 2023).
Addressing Risks
Managing offtake risks is also critical since the green hydrogen market is underdeveloped. Developers prefer long-term contracts, but off-takers often seek short-term deals due to the economics of green hydrogen. Instruments like payment security mechanisms and penalty clauses can protect producers. The EU’s contract-for-difference (CfD) scheme, which closes the price gap between green and grey hydrogen, offers a model India could adopt. Pilot projects in sectors such as shipping, long-haul mobility, and low-carbon steel are vital for investor confidence and should expand to include other industries like fertilizers. Co-locating projects with demand centres, like freight corridors, can improve scale and efficiency. Sharing lessons from these pilots will further industry participation (PIB, 2023).
Strengthening Domestic Manufacturing
Enhancing domestic manufacturing capabilities for electrolysers is essential to reducing dependency on imports. India currently relies heavily on imported electrolysers, but domestic manufacturing could cut costs and create jobs. The Production Linked Incentives (PLI) scheme can encourage investments by offering front-loaded rewards and clear sunset clauses, driving private sector engagement (Argus, 2023).
Demand-side interventions like emissions penalties could accelerate the shift to low-carbon technologies. Policies imposing carbon taxes or limiting emissions can help level the playing field between green and grey hydrogen. The EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) provides an example of protecting domestic industries while promoting clean energy (IRENA, 2020). Additionally, mandates and green product standards can stimulate demand for green hydrogen by allowing consumers to choose sustainable products. Sectors like oil refining and fertilizers could be required to replace grey hydrogen with green hydrogen, stimulating demand. Green Public Procurement (GPP) policies can further drive demand, with minimal impact on project costs. Using green steel in infrastructure, for example, would raise costs by just 0.15 percent (Mathur, 2013).
Storage and transportation challenges remain due to hydrogen’s low density and volatility, making it harder to handle than fossil fuels. Building a national pipeline infrastructure and investing in hydrogen storage facilities could reduce costs, but requires policy support. Government investment in research and development (R&D) is also essential for advancing storage solutions (PIB, 2023).
Lastly, hydrogen hubs or industrial clusters located around factories, renewable energy centers, and transmission infrastructure can create demand-supply synergies. Incentives for these clusters would speed up green hydrogen adoption and reduce risks for early movers (IRENA, 2020).
Developing a green hydrogen ecosystem in India requires both supply- and demand-side interventions. The GoI must take a systems approach that addresses regulatory barriers, enhances manufacturing capabilities, stimulates demand, and builds the necessary infrastructure to support a hydrogen economy. If these measures are implemented effectively, India could become a global leader in green hydrogen and significantly reduce its carbon footprint by 2070.
Note: The document has been developed jointly with Ashoka Centre for People Centric Energy Transition [ACPET].
(Vaibhav Chowdhary, Director, Ashoka Centre for People Centric Energy Transition [ACPET] and Vivek Jha, Independent Consultant at ACPET.)
Views are personal, and do not represent the stance of this publication.
Discover the latest Business News, Sensex, and Nifty updates. Obtain Personal Finance insights, tax queries, and expert opinions on Moneycontrol or download the Moneycontrol App to stay updated!
Find the best of Al News in one place, specially curated for you every weekend.
Stay on top of the latest tech trends and biggest startup news.