



The periodic table of elements is one of the most significant tools in science, organizing all known chemical elements in a structured and meaningful way. It helps scientists understand element properties, relationships, and behaviors. But who created this ingenious system, and how does it actually work? Read below to find out.
Who Created the Periodic Table of Elements?
The credit for creating the modern periodic table goes to Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, in 1869. While several scientists before him had attempted to classify elements, Mendeleev was the first to organize them systematically based on their atomic mass and properties. Mendeleev left gaps in his table for elements yet to be discovered, accurately predicting their existence and properties. His foresight was later validated when elements like gallium and germanium were discovered, fitting perfectly into his periodic table.
Other Contributors to the Periodic Table
Although Mendeleev's work was groundbreaking, the table evolved over time with contributions from other scientists:
How Does the Periodic Table Work?
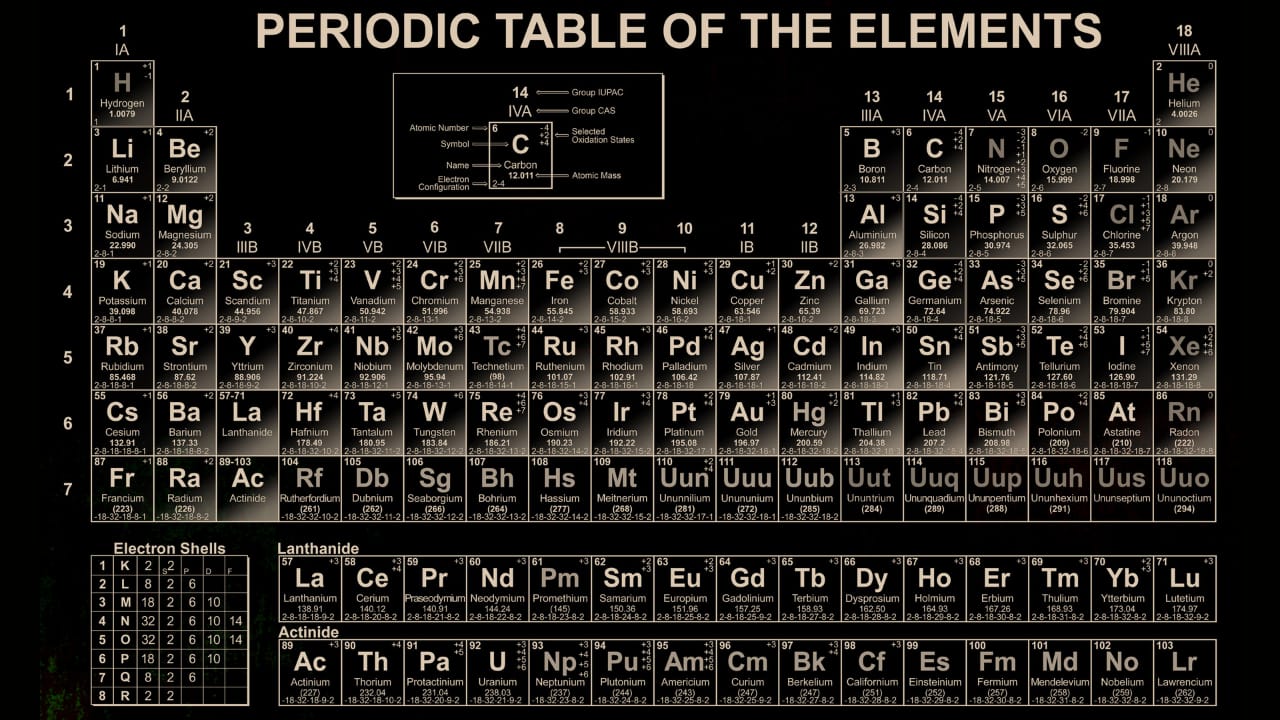
The periodic table is a grid-like structure where elements are arranged based on their atomic number (the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus) and grouped by similar chemical properties.
Structure of the Periodic Table
Categories of Elements
Why the Periodic Table is Useful
Discover the latest Business News, Sensex, and Nifty updates. Obtain Personal Finance insights, tax queries, and expert opinions on Moneycontrol or download the Moneycontrol App to stay updated!
Find the best of Al News in one place, specially curated for you every weekend.
Stay on top of the latest tech trends and biggest startup news.