


We are at the crossroads of convergence where various technologies merge together and make each other stronger.
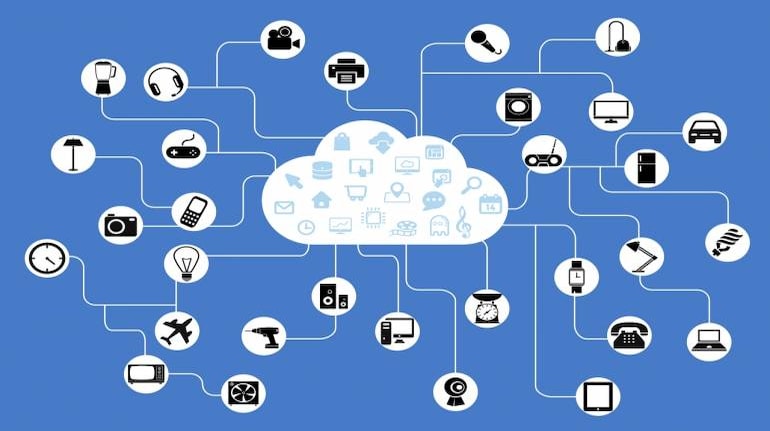
You may have heard about IoT (Internet of Things), a collective of networked devices that communicate with one another and the cloud, but have you ever wondered what the underlying technology is?
What is M2M communication?
In a broad sense, M2M or Machine-to-Machine Communication, refers to a standard of protocols that allow machines to interface and exchange information with one another, without the need for human intervention.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are what enable these interactions, letting machines make their own autonomous choices.
According to data by TechTarget, M2M was first used in manufacturing and industrial settings to facilitate remote monitoring functions and controlling equipment.
Over time, it seeped into other sectors like healthcare, business and insurance, with the most famous example being consumer IoT products.
Okay, but how does M2M work?
The main function of M2M is to facilitate smooth communication between various working components of a live network. This is done by tapping into the data collected by IoT devices and transmitting them to a network, which will then relay that information to the connected devices.
An M2M network is set up using public networks and access methods like cellular or Wi-Fi for more cost-effective solutions. The data is collected through sensors, RFID (radio frequency identification) or cellular communication.
The information is then fed to a software that enables autonomous decision- making. Once it’s analyzed, the M2M network can trigger pre-programmed automated actions based on the data received.
Sounds fancy, but what does this mean for India?
Besides the obvious smart-home applications for M2M, the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) has published detailed guidelines about M2M applications in various fields.
As per the guidelines, for a network to qualify as M2M, it should have a device with an M2M chip inside it, it should be able to log in to a network to provide connectivity and enable its functions, and there should be an underlying software that is able to interpret the data and trigger corresponding functions.
With this in mind, TRAI has listed potential services and industries that can benefit greatly from M2M. The first of this is the automotive industry.
M2M can enhance vehicle-tracking capabilities for manufacturers and cab services. It can help with navigation data for real-time maps, or help with fleet management. It can also be used in the manufacturing and logistics segments.
Another area that can be simplified using M2M is utility monitoring, such as smart metering for water and electricity bills, or gas and oil pipeline monitoring.
In health care, M2M can be deployed to help with medication tracking, organizing and collecting data from wearable devices, and to provide remote medical assistance to backward areas.
It also has applications in the safety and surveillance industries, like commercial and home security, providing data for surveillance applications, autonomous control over fire alarms and police/medical alerts, and dedicated network bands for women’s safety.
The financial and retail sector can use M2M for Point-of-Sale (POS) services, ATMs, vending machines, digital signage, kiosks and handheld terminals.
M2M is already a large part of various smart home projects in India, which use the technology for waste management, street light control, water distribution and smart parking.
The agriculture sector can benefit greatly from remote-controlled equipment like irrigation pumps, and it can be used to analyze and monitor soil data to better predict the harvest.
All of this sounds great, but what are the drawbacks?
M2M-enabled networks and machines are expected to perform autonomously. This can help speed up several processes without human intervention. You also face an increased risk of security intrusions like data breaches or unauthorized monitoring of data, if the network is taken over.
Another logistical problem is that as the network grows bigger and the more hardware is added to it, it becomes nearly impossible to physically maintain all of them, necessitating remote management.
With large networks, it becomes very difficult to service old equipment on time, leaving them and the network vulnerable to intrusions.
The solution, for now, is to make specialized tamper-proof equipment for larger networks and embedding security protocols into the hardware itself.
The communication should also be encrypted, preventing snooping and the network should be deployed on secure servers.
Another way to combat these problems is to segment M2M devices off in their own network, while managing confidentiality and device identity through software.
Discover the latest Business News, Sensex, and Nifty updates. Obtain Personal Finance insights, tax queries, and expert opinions on Moneycontrol or download the Moneycontrol App to stay updated!
Find the best of Al News in one place, specially curated for you every weekend.
Stay on top of the latest tech trends and biggest startup news.