



Beaches, backwaters, excellent hospitality and thriving tourism industry have long been the hallmarks of Goa and Kerala. The two states on India's western periphery can now boast of another virtue -- women's safety. Women in Goa and Kerala are safest while those in Bihar and Uttar Pradesh are most vulnerable, a new report states.
On a metric termed Gender Vulnerability Index (GVI), Goa ranks as the safest region for women in India, followed by Kerala. The former leads with healthy 0.656, while the southern state takes the second spot with 0.634 on the index structured by NGO Plan India and released by Women and Child Development Ministry.
The index ranks states on four key parameters -- education, poverty, protection and health.
Here are the GVI rankings for all states:
[caption id="attachment_2428571" align="alignleft" width="633"]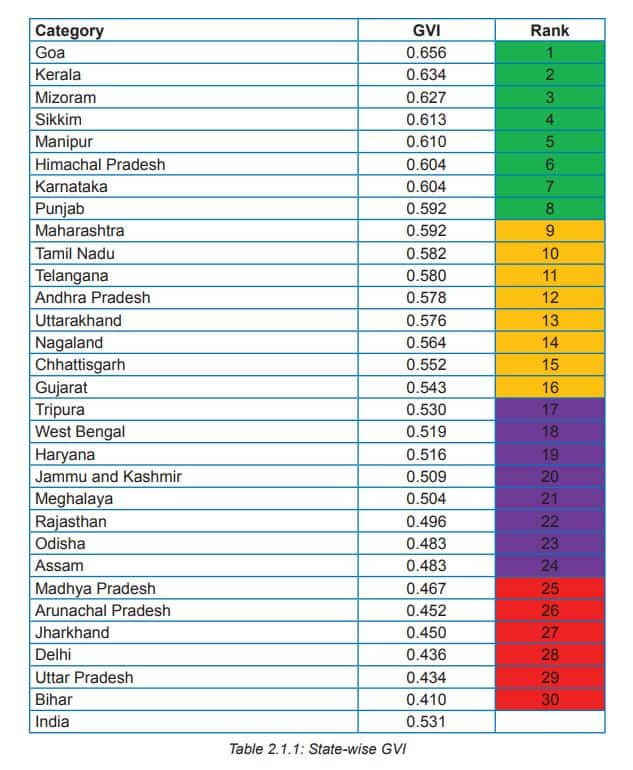 Courtesy: Gender Vulnerability Index report[/caption]
Courtesy: Gender Vulnerability Index report[/caption]
The index follows a Lifecycle approach according to which challenges faced by women are unique and continue throughout their life.
The last spot on the list is taken by Bihar (0.410) where are most vulnerable in terms of health and poverty. As per the data collated by the report, nearly 12.2 percent girls, aged 15-19 in the state, were either pregnant or mothers. Not only that, 39 percent of the girls in the state get married before the legal age.
Out of the list of 30 cities, Delhi comes at 28 with a GVI of 0.436 with it getting poorest score in the education department.
Protection is at the heart of Plan India's lifestyle approach. While Goa tops the list in protection with GVI of 0.848, Uttar Pradesh is last at 30 with GVI of 0.48.
Delhi is at 28 with a GVI of 0.520. Punjab, Tripura and Himachal Pradesh make it to top of the list while Delhi, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar are the worst performing on .
"Nearly a third of all rape victims are girls under the age of 18. Sources expect the demographic crises is likely to exacerbate abuse and the dwindling sex ratio is likely to continue to fall. These dilemmas are not just social, they are ethical violations of one’s human security," the report said.
The report further says that while India has shown some progress, there is still a long way to go. Nearly a third of married women have reported experiencing spousal violence.
[caption id="attachment_2428573" align="alignleft" width="614"]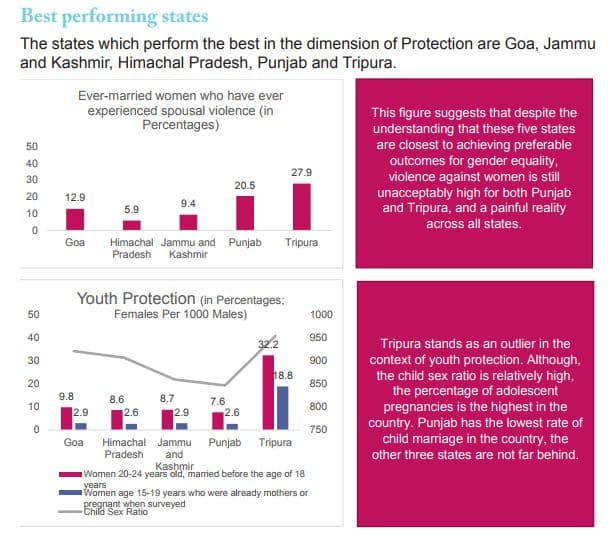 Courtesy: Gender Vulnerability Index report[/caption]
Courtesy: Gender Vulnerability Index report[/caption]
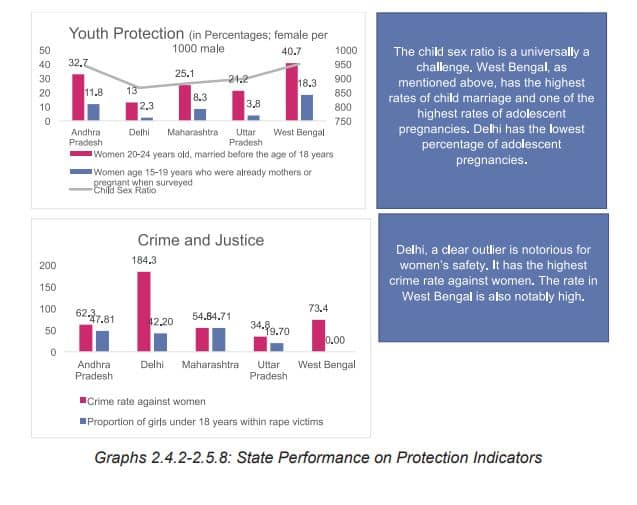
There are several regional disparities as well. "The regional disparities for crimes against women are appallingly high, nationally the figure stands at 53.9 percent, in states like Assam and Delhi this rate crosses over 140 percent," it said.
In West Bengal, rate of child marriages are over 40 percent while in Punjab, it is estimated to be lower than 8 percent.
 Education
EducationIn education, the best performing states are Maharashtra, Punjab, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh and Goa. While gender ratio is poor in Punjab and Maharashtra, dropouts at primary schooling is below the national average in all five cities.
However, dropout rate in secondary school is very high in Sikkim and Maharashtra. All states, except Sikkim, also fail in providing basic facilities of toilets and boundary wall to students.
[caption id="attachment_2428619" align="alignleft" width="614"]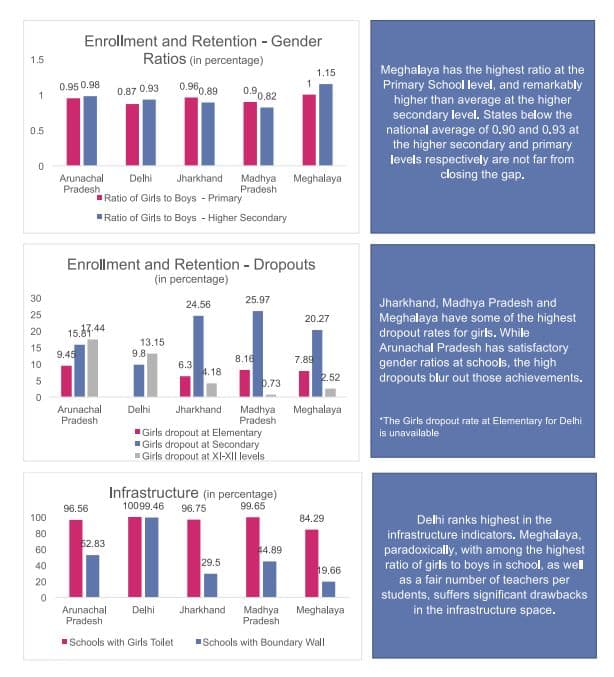 Courtesy: Gender Vulnerability Index report[/caption]
Courtesy: Gender Vulnerability Index report[/caption]
In education, the poor performing states include Delhi, Madhya Pradesh, Meghalaya, Jharkhand, Arunachal Pradesh.
Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand and Meghalaya tops the dropout list for girls.
HealthWhile India has progresses in terms of infant mortality rate and neonatal factors, preventable diseases continues to be a big cause of concern for girls and women.
"Plan's lifecycle approach lists malnutrition as a chief concern among young women. This lack of subsistence is a violation of a girls most fundamental needs and can affect her throughout the life course," the report said.
Reach is still shortsighted in maternal health and the reach for it is still "formidable challenge as intended beneficiaries are being excluded, this is reflected in the Gender Vulnerability Index."
[caption id="attachment_2428583" align="alignleft" width="638"] Courtesy: Gender Vulnerability Index report[/caption]
Courtesy: Gender Vulnerability Index report[/caption]
Anemia is another serious concern for young children, adolescent girls and pregnant women. There are several gaps still in the female, maternal health and child development, as per the GIV data.
While Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Sikkim, Andhra Pradesh rank the highest in health, states like Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Bihar and Meghalya fail to meet the norms.
Girls in Bihar, Jharkhand and Haryana are most malnourished with 40 percent underweight and more than 60 percent anemic girls in these states.
PovertyThe report highlights unequal access to women in terms of financial services and use of information and communication technology. While Manipur tops the list, Bihar comes at the last position with poverty GVI of 0.31.
Only the north east and south states tops the list in poverty. While in Manipur, nearly 70 percent women own land, high rate of poverty is a matter of concern. Mizoram has the lowest poverty headcount ratio.
[caption id="attachment_2428617" align="alignleft" width="627"]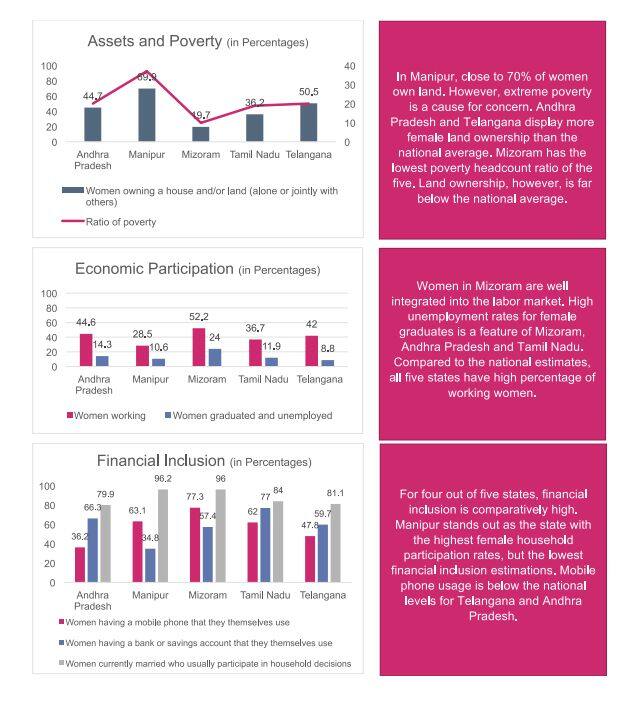 Courtesy: Gender Vulnerability Index report[/caption]
Courtesy: Gender Vulnerability Index report[/caption]
In terms of poverty, Bihar, Jammu and Kashmir, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh rank the lowest in terms of poverty. Uttar Pradesh has high poverty headcount as well as low rate of land ownership.
J&K has the lowest number of working women.
Discover the latest Business News, Sensex, and Nifty updates. Obtain Personal Finance insights, tax queries, and expert opinions on Moneycontrol or download the Moneycontrol App to stay updated!
Find the best of Al News in one place, specially curated for you every weekend.
Stay on top of the latest tech trends and biggest startup news.