10 warning signs your thyroid hormones may be out of control
Thyrotoxicosis is caused by elevated levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), often due to hyperthyroidism. Symptoms include weight loss, increased appetite, palpitations, breathlessness, tremors, sweating, and eye bulging. Diagnosis involves thyroid function tests and antibody levels.
1/10
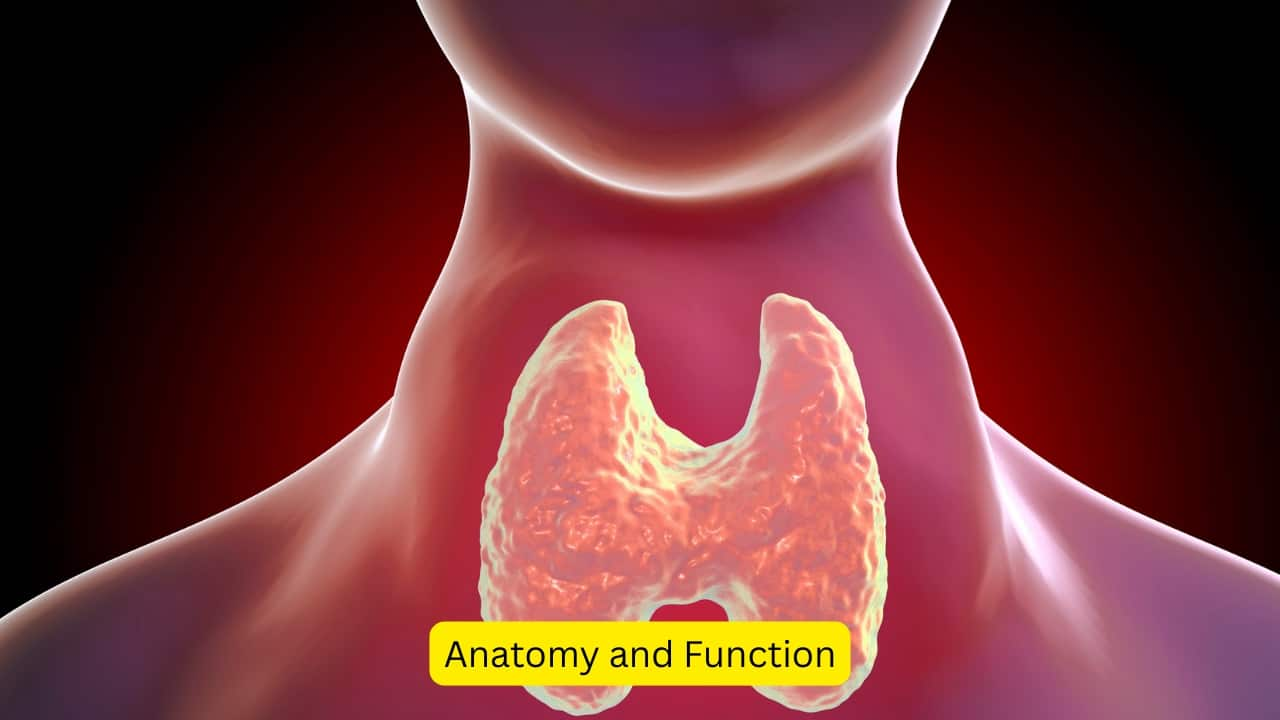
Anatomy and Function
The thyroid is a butterfly shaped gland present in the anterior part of the neck, below the Adam’s apple. It consists of a right and left lobe, joined together by the isthmus. The hormones it produces influence metabolism, growth and development, along with the nervous system.(Image: canva)
The thyroid is a butterfly shaped gland present in the anterior part of the neck, below the Adam’s apple. It consists of a right and left lobe, joined together by the isthmus. The hormones it produces influence metabolism, growth and development, along with the nervous system.(Image: canva)
2/10
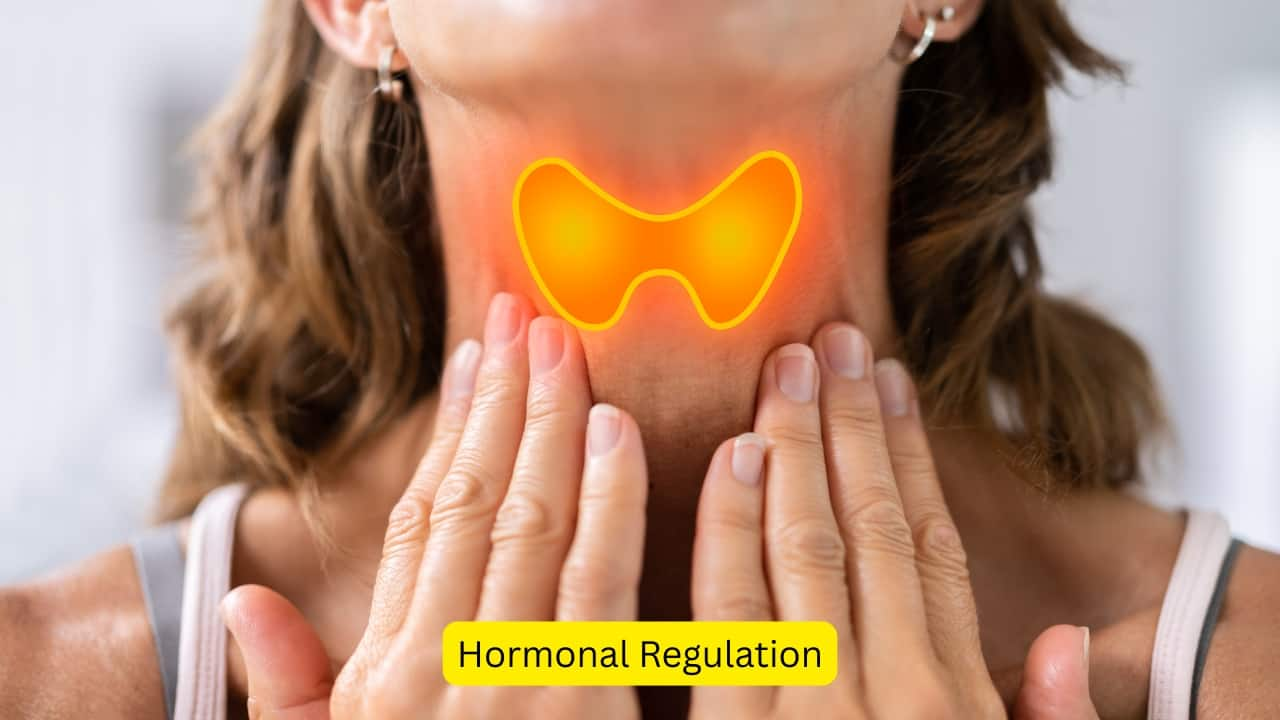
Hormonal Regulation
The master gland, the pituitary, secretes a hormone known as the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which causes the release of the thyroid hormones, namely, triiodothyronine (T3), and tetraiodothyronine (T4), which is also known as thyroxine. These hormones are responsible for various processes in the body.(Image: canva)
The master gland, the pituitary, secretes a hormone known as the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which causes the release of the thyroid hormones, namely, triiodothyronine (T3), and tetraiodothyronine (T4), which is also known as thyroxine. These hormones are responsible for various processes in the body.(Image: canva)
3/10
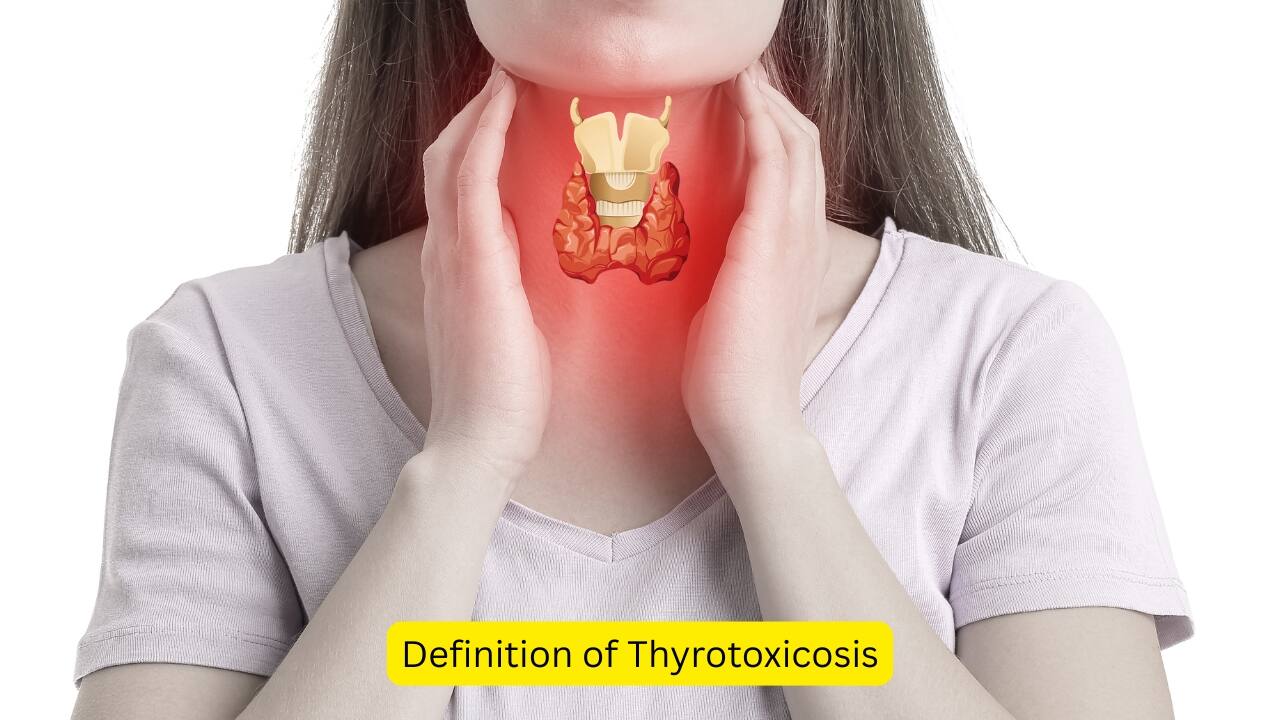
Definition of Thyrotoxicosis
Increased levels of circulating thyroid hormones T3 and T4 can lead to a state known as thyrotoxicosis. This increase is either attributed to destruction of the thyroid gland or a different source (other than the thyroid) secreting these hormones. A number of causes can lead to thyrotoxicosis.(Image: canva)
Increased levels of circulating thyroid hormones T3 and T4 can lead to a state known as thyrotoxicosis. This increase is either attributed to destruction of the thyroid gland or a different source (other than the thyroid) secreting these hormones. A number of causes can lead to thyrotoxicosis.(Image: canva)
4/10

What is Hyperthyroidism
The clinical result of the excessive circulating thyroid hormones is known as hyperthyroidism, and is the most common reason for the development of thyrotoxicosis. Hyperthyroidism may be a result of excess consumption of iodine, or diseases like Graves’ disease and Plummer’s disease.(Image: canva)
The clinical result of the excessive circulating thyroid hormones is known as hyperthyroidism, and is the most common reason for the development of thyrotoxicosis. Hyperthyroidism may be a result of excess consumption of iodine, or diseases like Graves’ disease and Plummer’s disease.(Image: canva)
5/10
Medication and Radiation Effects
People who take medication for treating arrhythmia, like amiodarone, may also develop hyperthyroidism. Alongside, those who have had an exposure to radiation are also susceptible. A psychiatric disorder that occurs due to excessive intake of thyroxine, known as thyrotoxicosis factitia, can also lead to features of hyperthyroidism.(Image: canva)
People who take medication for treating arrhythmia, like amiodarone, may also develop hyperthyroidism. Alongside, those who have had an exposure to radiation are also susceptible. A psychiatric disorder that occurs due to excessive intake of thyroxine, known as thyrotoxicosis factitia, can also lead to features of hyperthyroidism.(Image: canva)
6/10

Physical Examination Findings
The thyroid, on examination, may show a diffuse enlargement, and the skin over the glands may be warm to touch. An abnormal whooshing sound may be heard over the glands through the stethoscope by the healthcare provider. This sound is a result of increased blood supply and vessels.(Image: canva)
The thyroid, on examination, may show a diffuse enlargement, and the skin over the glands may be warm to touch. An abnormal whooshing sound may be heard over the glands through the stethoscope by the healthcare provider. This sound is a result of increased blood supply and vessels.(Image: canva)
7/10

Symptoms: Appetite and Digestive
The affected individual may experience an increased appetite, however, they may lose weight instead of gaining it. Vomiting and an increased frequency of stools, and even loose stools may be seen. The person may have shortness of breath on exertion and chest pain as well.(Image: canva)
The affected individual may experience an increased appetite, however, they may lose weight instead of gaining it. Vomiting and an increased frequency of stools, and even loose stools may be seen. The person may have shortness of breath on exertion and chest pain as well.(Image: canva)
8/10

Cardiac Symptoms
An increased pulse rate, palpitations (the awareness of one’s own heart beat), and symptoms of cardiac failure may also be observed. Hyperthyroidism can lead to irregular beating of the heart and heart murmurs too. The person may seem nervous, irritable and emotionally labile.(Image: canva)
An increased pulse rate, palpitations (the awareness of one’s own heart beat), and symptoms of cardiac failure may also be observed. Hyperthyroidism can lead to irregular beating of the heart and heart murmurs too. The person may seem nervous, irritable and emotionally labile.(Image: canva)
9/10

Neurological and Skin Symptoms
Fine tremors are seen in people with hyperthyroidism, along with an inability to concentrate. The skin may feel soft and moist to touch, and affected persons sweat much more than usual. Hair loss and intolerance to heat are also commonly seen, with bulging of the eyes.(Image: canva)
Fine tremors are seen in people with hyperthyroidism, along with an inability to concentrate. The skin may feel soft and moist to touch, and affected persons sweat much more than usual. Hair loss and intolerance to heat are also commonly seen, with bulging of the eyes.(Image: canva)
10/10
Diagnosis and Management
The healthcare provider must be consulted if such symptoms are seen. They may advise certain laboratory investigations like free T3 and T4 levels, along with TSH levels. Certain antibodies may also be tested for, like the TSH receptor antibody. Medical and surgical management may be recommended.(Image: canva)
Disclaimer: This article, including health and fitness advice, only provides generic information. Don’t treat it as a substitute for qualified medical opinion. Always consult a specialist for specific health diagnosis
The healthcare provider must be consulted if such symptoms are seen. They may advise certain laboratory investigations like free T3 and T4 levels, along with TSH levels. Certain antibodies may also be tested for, like the TSH receptor antibody. Medical and surgical management may be recommended.(Image: canva)
Disclaimer: This article, including health and fitness advice, only provides generic information. Don’t treat it as a substitute for qualified medical opinion. Always consult a specialist for specific health diagnosis
Discover the latest Business News, Budget 2025 News, Sensex, and Nifty updates. Obtain Personal Finance insights, tax queries, and expert opinions on Moneycontrol or download the Moneycontrol App to stay updated!





