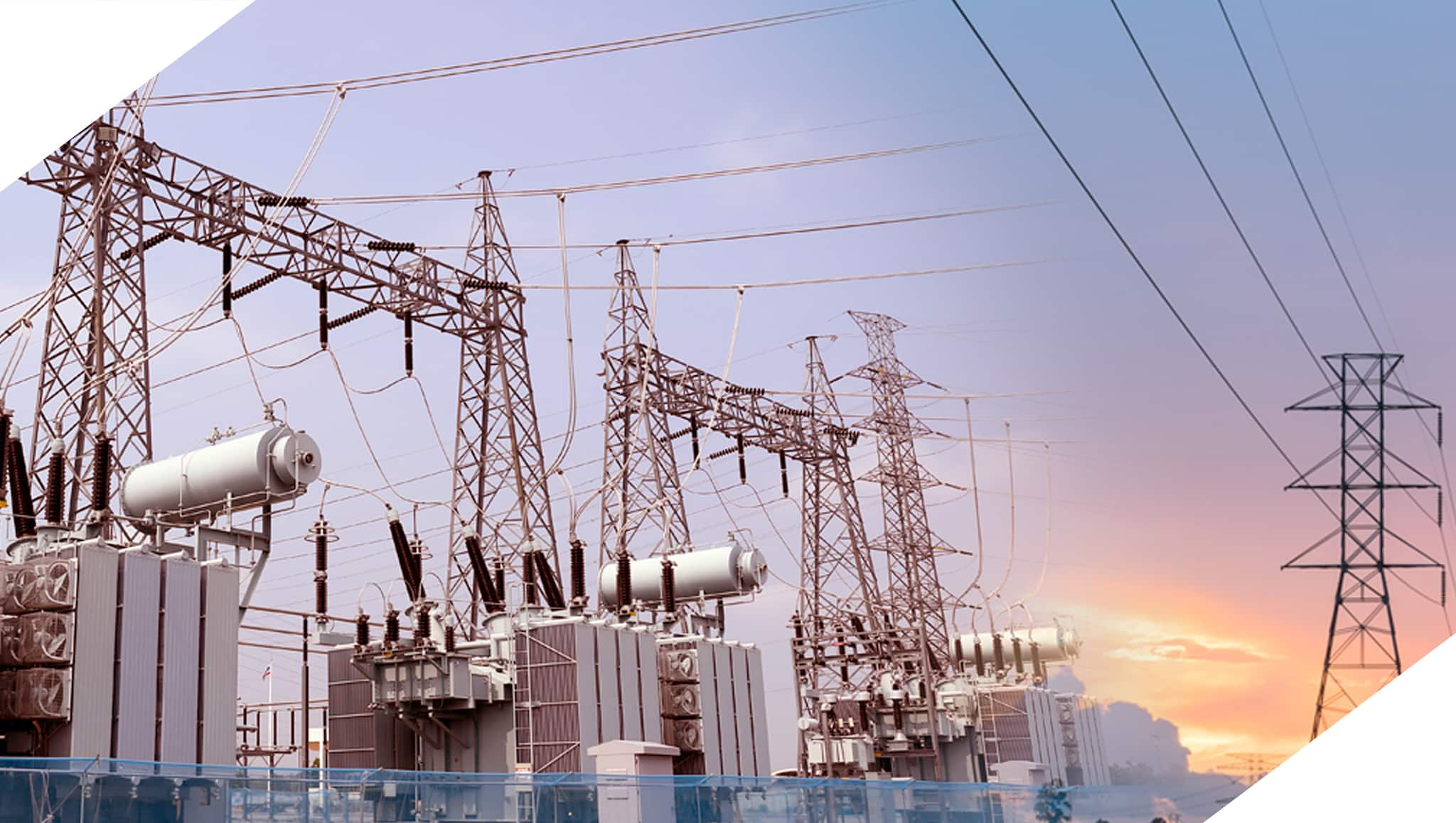
Electricity consumption in India has reportedly almost tripled over the last two decades due to rapid urbanization and rising incomes. Significantly, more than half a billion people have been connected to the power grid over the last decade, with the Government stepping up its mission to ensure Power for All.
Apart from significant domestic consumption, commercial industry, agriculture, infrastructure, and utility sectors are also major power consumers driving demand year after year.
The peak power demand met or the maximum supply for a day on June 30, 2021 reached 191.51 gigawatts (GW), an increase of 16 percent from the 164.98 GW observed in June 20201, as per reports. Many analysts believe that electricity demand will outstrip the overall energy requirement in the coming years.
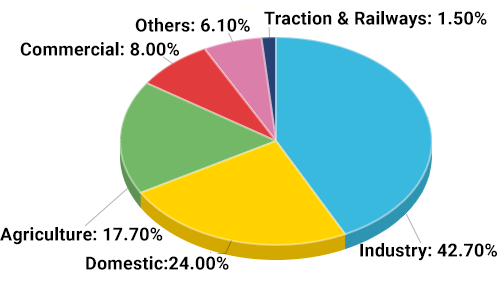
Sector-wise FY 2020 pan-India electricity consumption2
Ramping-up Power Generation, Transmission & Distribution
To meet the surging power demand and expedite development, the Government has taken several initiatives to boost power generation capacity across thermal, hydropower, nuclear, and renewable sources. In addition to improving existing operations, it is also focusing on adding new hydroelectric and thermal projects.
Nevertheless, the key underlying theme of the present electricity policy is to move towards clean, renewable energy sources such as water, wind, and solar, thus reducing dependency on fossil fuels to secure a carbon-neutral future.
According to Central Electricity Authority (CEA) data, the national electric grid had an installed capacity of 383.37 GW as of 31 May 2021, of which 95.65 GW was generated using renewable sources, including small hydro projects, biomass power, urban & industrial waste power, solar and wind energy3.
However, despite an impressive all-India installed capacity in power stations today, many consumers still grapple with intermittent electricity supply and outages during peak periods. Among various factors, transmission and distribution losses are also significant causes of under-served power demand.
Reliability, Technology & Sustainability: 3 Keys to Electricity Security
The Government’s drive for private investments and Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) has certainly put power infrastructure and capacity building, adoption of advanced power products and technologies on a fast track.
As India pursues a robust, reliable, and more sustainable power future, global automation, and technology pioneer Hitachi Energy, continues to play a pivotal role in transforming India’s power paradigm.
Driven by Social, Environmental, and Economic values, Hitachi Energy has created a bevy of avant-garde grid automation, grid integration, high-voltage components, and high-tech transformer solutions that are proving to be revolutionary.
Offering an optimal solution, Hitachi Energy compact indoor and underground substations are multi-faceted and aesthetically designed to merge into their immediate environment.
Hitachi Energy hi-tech, space conserving substation solutions
These customizable, space-conserving installations also take care of noise emissions and other environmental concerns.
Enhancing Industrial Power Distribution System(s)
Uninterrupted, high-quality power supply is a primary concern for industrial consumers as it affects productivity and operational efficiency.
Source:
1. https://energy.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/power/indias-power-demand-surges-to-all-time-high-crosses-200-gw-mark/84236469
2. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1130112/india-electricity-consumption-share-by-sector/
3. https://cea.nic.in/wp-content/uploads/installed/2021/05/installed_capacity.pdf
4. https://www.businesstoday.in/industry/energy/story/indias-power-consumption-jumps-nearly-25-to-2624-bu-in-first-week-of-may-295405-2021-05-09












